Acne treatment
Acne treatment involves a combination of topical, oral, and lifestyle interventions to manage and prevent acne breakouts.

Topical Treatments:
Retinoids: Derivatives of vitamin A, like tretinoin or adapalene, help unclog pores and prevent the formation of new acne lesions.
Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills bacteria on the skin and reduces inflammation.
Topical Antibiotics: Antibiotic creams or gels, such as clindamycin or erythromycin, can help control bacterial growth.
Oral Medications:
Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics like doxycycline or minocycline are prescribed for moderate to severe acne to reduce inflammation and bacterial infection.
Birth Control Pills: For females, hormonal birth control can regulate hormones and improve acne in some cases.
Isotretinoin (Accutane): A powerful oral retinoid reserved for severe, persistent acne. It requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects.

Lifestyle and Skincare Practices:
Procedural Treatments:
Chemical Peels: In-office chemical peels exfoliate the skin, unclog pores, and promote skin renewal.
Microdermabrasion: Mechanical exfoliation to remove the top layer of dead skin cells.
Laser and Light Therapies: These can target bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Consultation with Dermatologist:
For severe or persistent acne, consultation with a dermatologist is essential to determine the most effective treatment plan.
Providing information on proper skincare, the importance of adherence to treatment regimens, and realistic expectations is crucial for successful acne management
Its important to note that individual responses to treatments vary, and finding the most effective combination may require some trial and error. Patience and consistency are key in managing acne effectively. Always consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan based on the severity and type of acne.
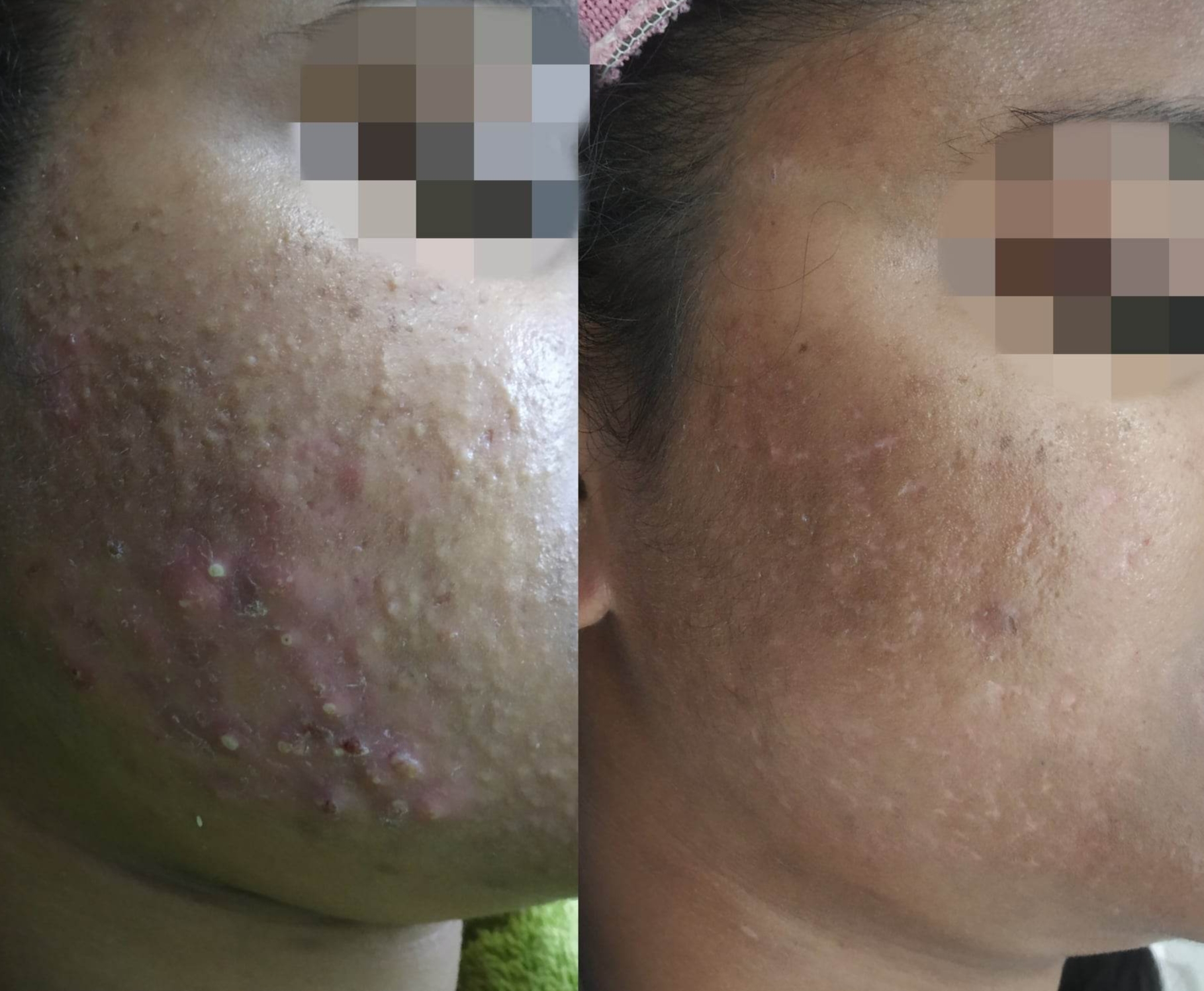
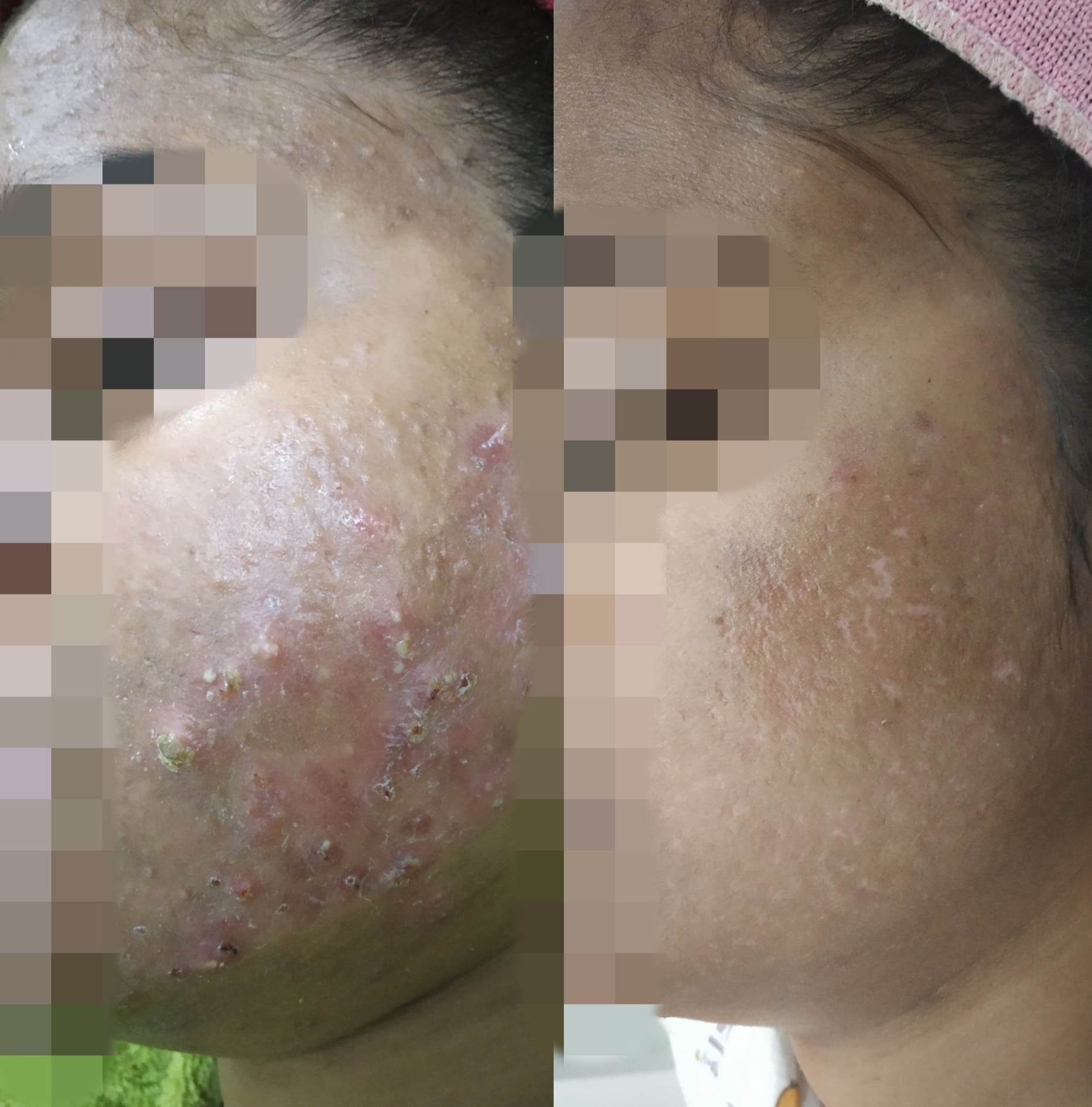
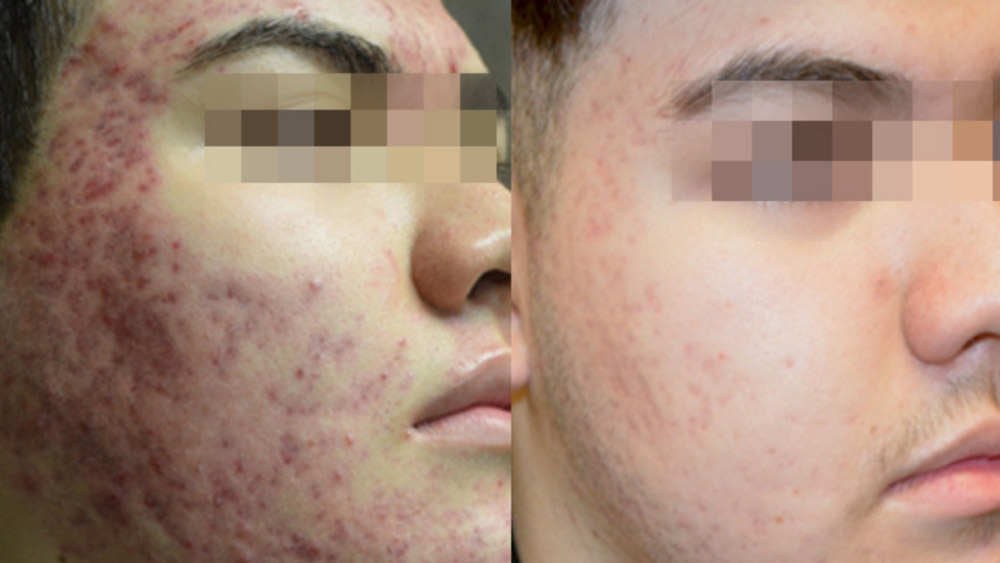
Before & After Acne Treatment