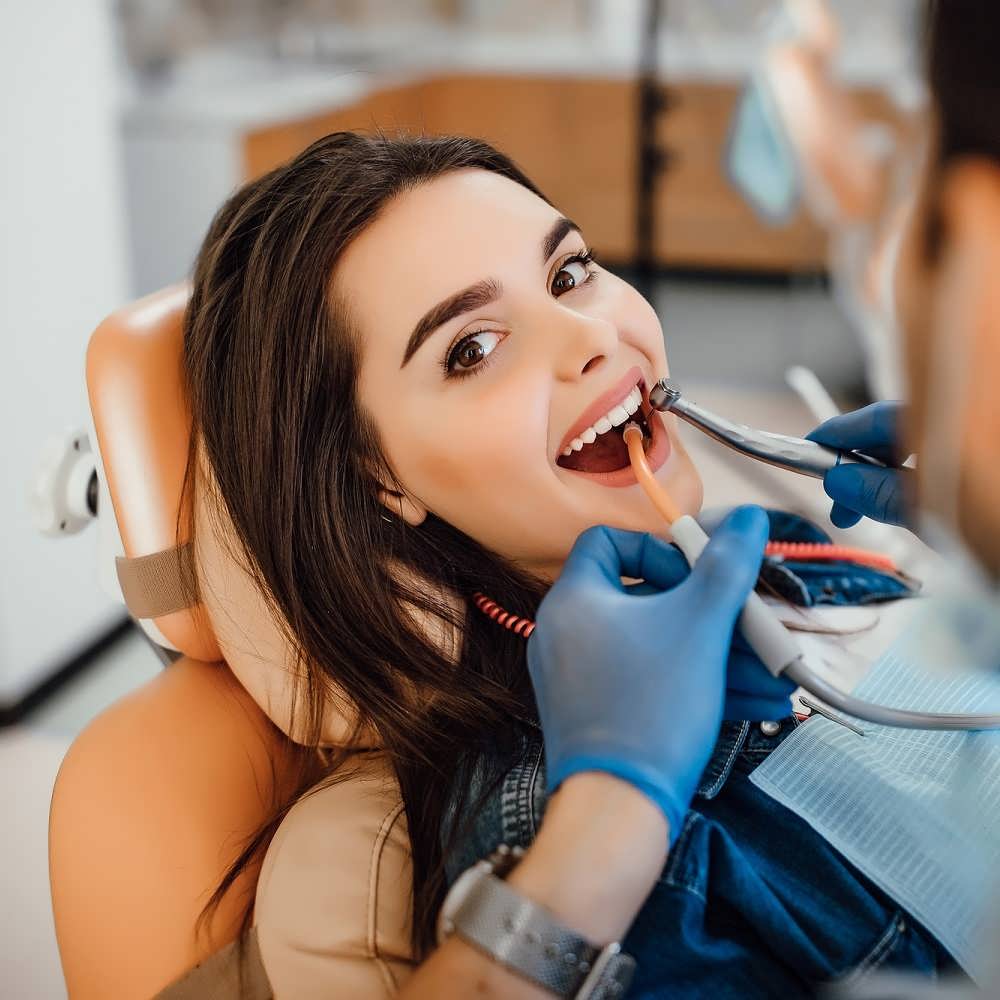
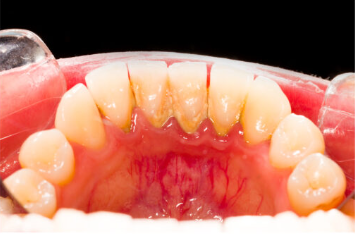
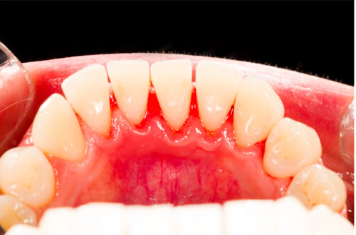
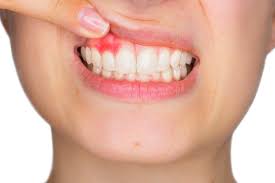
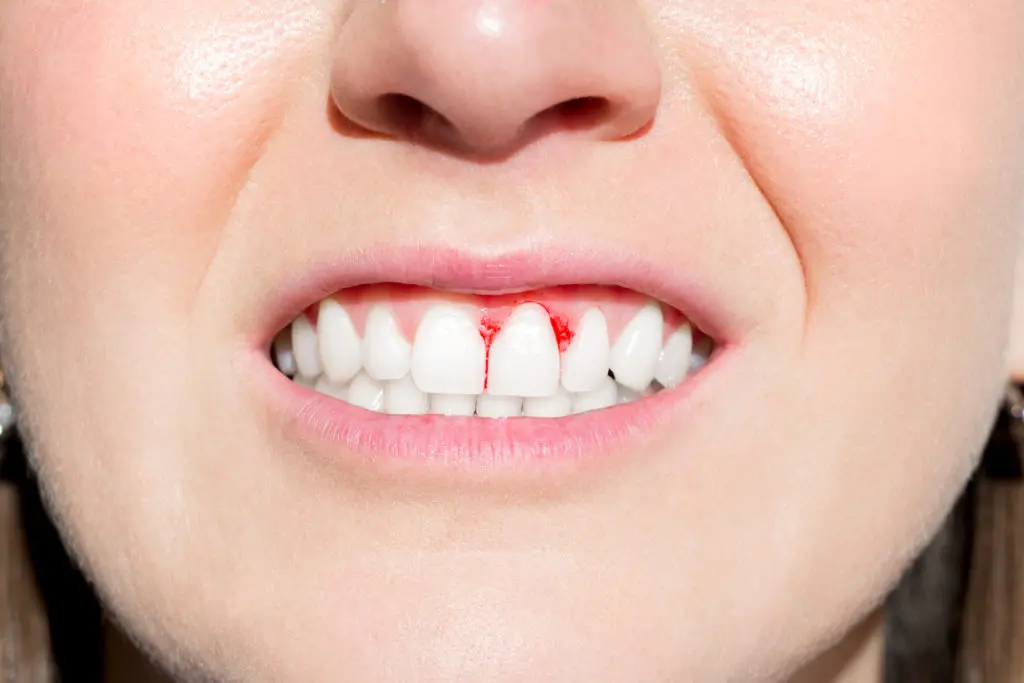
Bleeding gums
Bleeding gums can be indicative of various underlying dental issues and should be addressed promptly to maintain oral health. Bleeding gums are a common dental concern that can be a sign of gum disease or other oral health issues.
- Professional dental cleaning helps remove plaque and tartar, reducing inflammation and bleeding.
- Consultation with a dentist is essential for a proper diagnosis and to determine the underlying cause of bleeding gums.
Importance of Treatment:
Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent further complications, such as tooth loss and systemic health issues linked to gum diseases.
Improving Oral Hygiene:
Patients are often advised to brush teeth twice daily, floss regularly, and use an antiseptic mouthwash to maintain good oral hygiene.
Soft Toothbrush and Technique:
Switching to a soft toothbrush and using gentle brushing techniques can prevent further irritation.
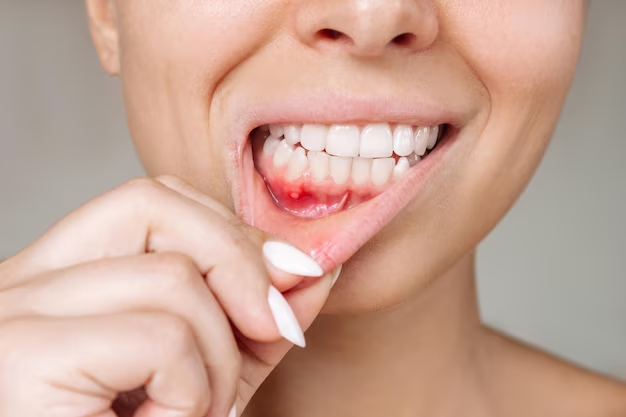
Flossing Techniques:
Proper flossing techniques are essential to remove plaque and debris from between teeth and along the gumline.
Antimicrobial Mouthwashes:
Dentists may recommend antimicrobial or medicated mouthwashes to control bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Dietary Changes:
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, can promote gum health.
Smoking Cessation:
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease; quitting can significantly improve oral health.
Scaling and Root Planing:
For more advanced cases, dentists may perform scaling and root planing to remove plaque and smooth root surfaces.
Laser gum Treatment
Painless laser gum Treatment for bleedding gums. .
Medications:
Antibiotics or prescription mouthwashes may be prescribed to control bacterial infections associated with gum disease.
Surgical Interventions:
In severe cases, surgical procedures like gum grafts or flap surgery may be necessary to treat advanced gum disease.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Encouraging lifestyle changes, such as stress management and regular exercise, can contribute to overall gum health.
Children and Adolescents:
Teaching proper oral hygiene habits early is crucial for preventing bleeding gums in children and adolescents.
Counseling and Support:
Providing emotional support and counseling can be beneficial, especially for individuals dealing with chronic gum conditions.
Emergency Care:
Advancements in dental technology contribute to more effective and less invasive treatments for bleeding gums. Immediate attention is necessary for sudden and severe bleeding; emergency dental care may be required in such cases.
Orthodontic Considerations:
Addressing misaligned teeth through orthodontic treatment can contribute to better oral health and reduce the risk of bleeding gums.
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism):
Managing bruxism, a condition where individuals grind their teeth, is important to prevent gum damage and bleeding.
Before & After Picture Gallery
Poor Oral Hygiene Gum Disease:
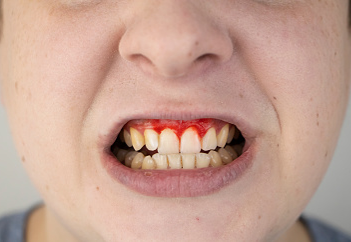
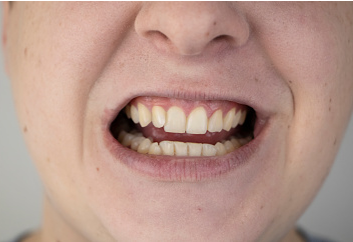
Inner Mouth Bleeding Gum Disease